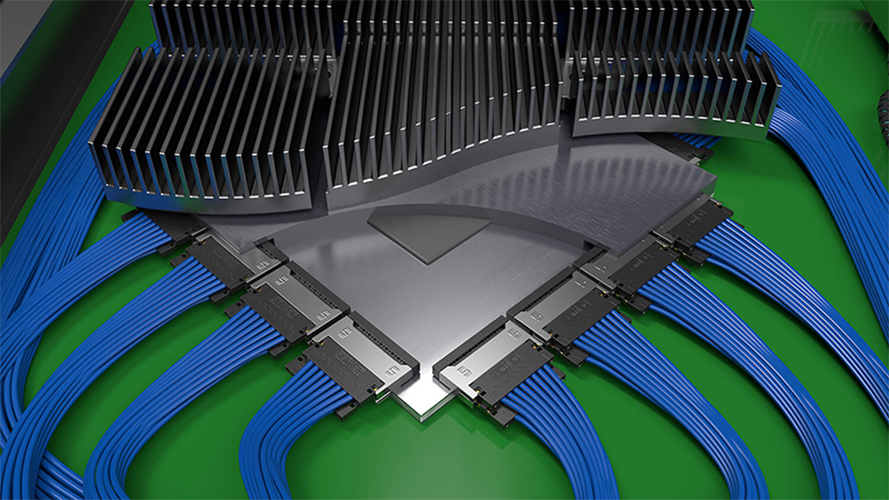
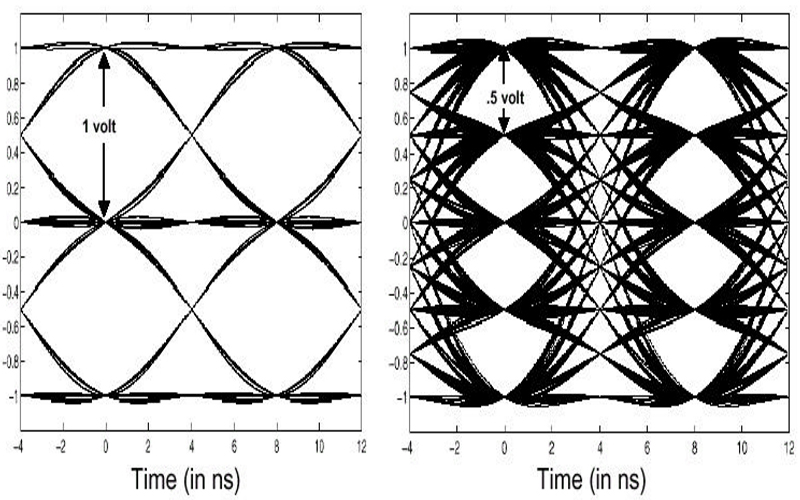
Designing 224 Gigabits per second four-level pulse amplitude modulation (224 Gbps-PAM4) interconnects is challenging. But it’s required to support the demands of generative artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), 1.6 Terabits per second (Tbps) networking, and other high-speed applications in advanced data centers, as well as 5G and 6G communications infrastructure. At these elevated data…
How does 4D-PAM5 work in Gigabit Ethernet?
Networks using 10 GbE rely on more sophisticated modulation and coding techniques than networks needed at lower data rates. 4D-PAM5 (four-dimensional five-level pulse amplitude modulation) are the encoding and modulation techniques used in Gigabit Ethernet (GbE). 4D-PAM5 replaced the multilevel transmit MLT-3 encoding and modulation used for 100BASE-TX. IEEE 1000BASE-T (GbE) uses a combination of…
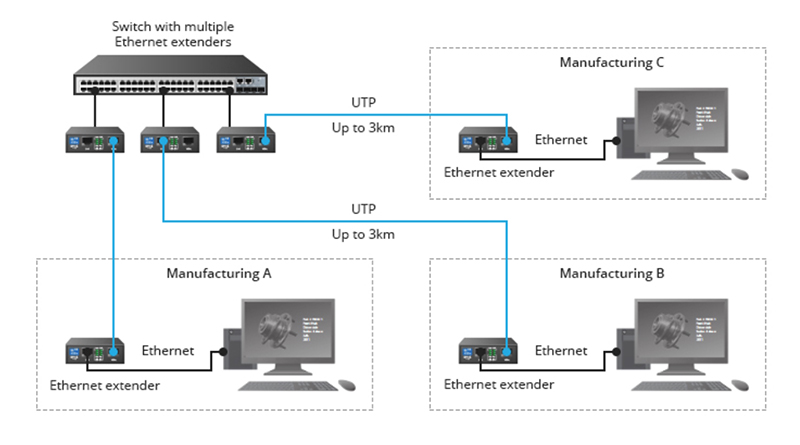
What’s the difference between an Ethernet extender and a media converter?
Extend the reach of Ethernet by converting the signals to different electrical or optical signals. Ethernet extenders and media converters can both be used to expand network coverage. Extenders operate over unshielded twisted pair (UTP) or coaxial cabling, while media converters change the signals from electrical to optical and back. Extenders and media converters can…
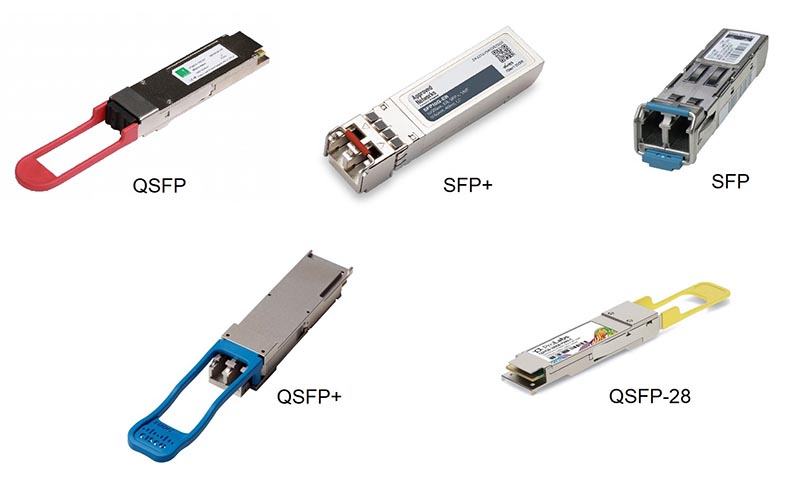
How do SFP, SFP+, and QSFP compare?
Pluggable modules come in many variants, each designed for a specific purpose. Small form factor pluggable (SPF) technology was developed to support high-speed interconnects between servers, storage, and communications equipment in data centers and similar environments. Over time, the multi-source agreement (MSA) that specifies SPF has evolved to include new formats, including SFP, SFP+, SFP28,…
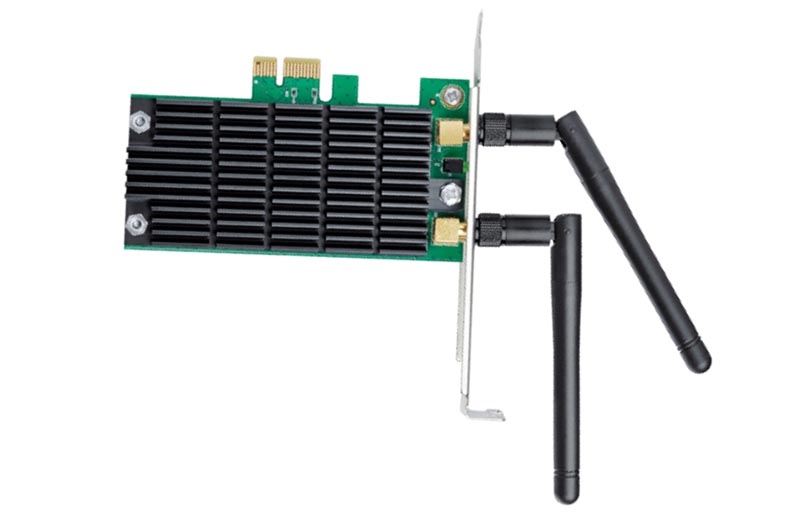
What’s a PCIe wireless adapter?
PCIe wireless adapters are one of the ways to connect a computer or server to a Wi-Fi network. There are different formats of PCIe wireless adapters, and there are also USB wireless adapters that compete with them based on convenience of operation. This FAQ reviews the operation of PCIe expansion cards, reviews the use of…
3D print 5G antennas
3D printing a mmWave antenna let’s you quickly build prototypes.
What is 5G femto application platform interface (5G FAPI)?
The 5G femto application platform interface (5G FAPI, or simply FAPI) published by the Small Cell Forum (SCF) is a suite of specifications that enable small cells to be built up piece-by-piece using components from different suppliers. It can be viewed as a subset of the network functional application platform interface (nFAPI), also published by…
Unlicensed spectrum use: What’s the technology behind it?
Unlicensed LTE lets wireless carriers offload traffic to Wi-Fi frequencies, but it must coexist with Wi-Fi and not interfere. Here’s how it works.
mmWave signals: The effect on PCB traces, cables and connectors
The use of mmWave technology is growing across various applications, from 5G telephony to automotive systems and drones. At mmWave frequencies, signal integrity (SI) is a major concern. SI measures the signal’s ability to propagate without distortion or undue losses. It measures the quality, or distortion, of the signal passing through the printed circuit board…