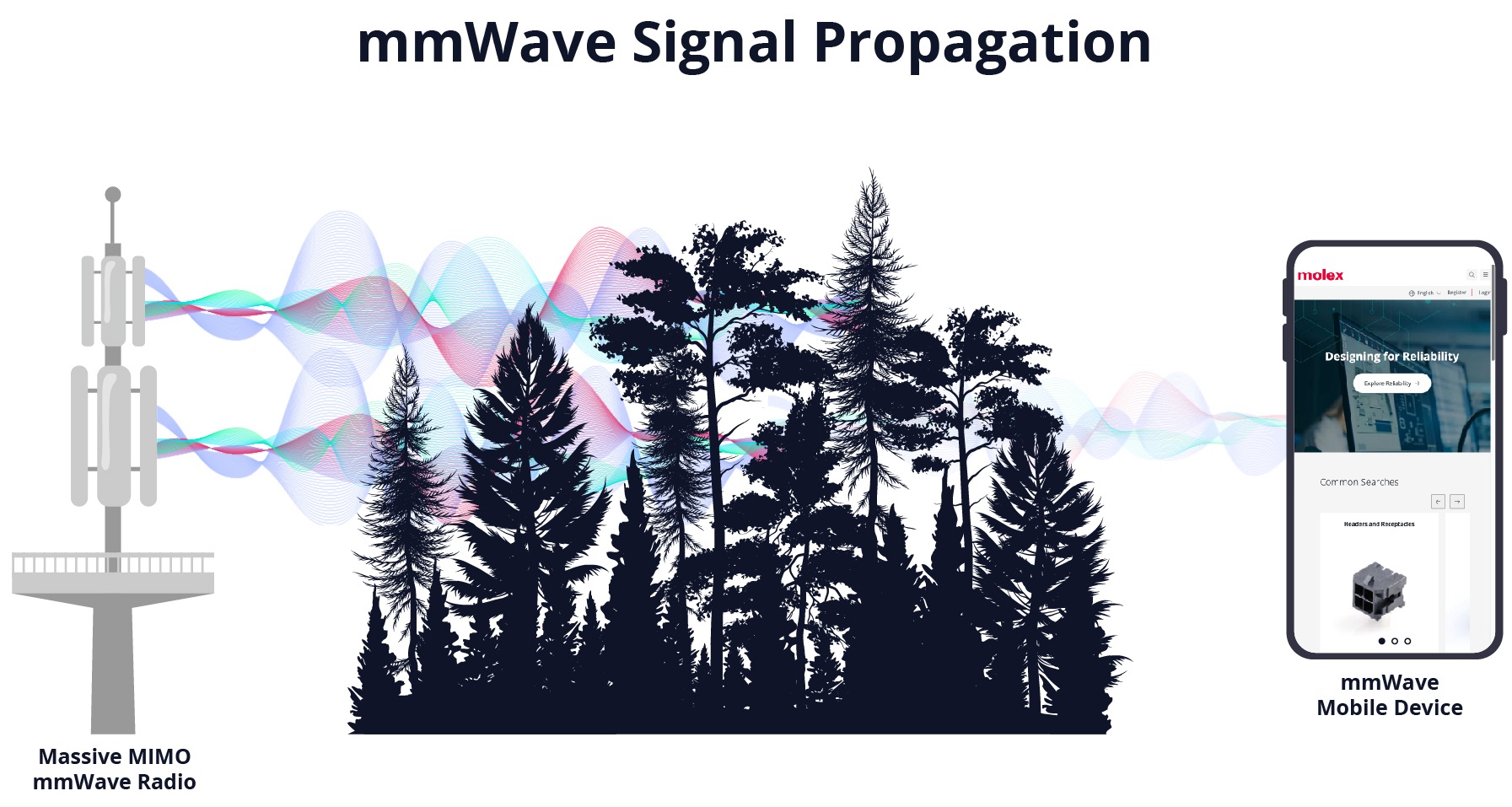
Millimeter-wave signals used in 5G networks provide wide bandwidth and high data rates. Signal losses, both over the air and through interconnects, bring design challenges.
mmWaves bring interconnect challenges to 5G and 6G
Signals in the mmWave range require extra care and more expensive components than at sub-6 GHz frequencies.
Front-end mmWave IC combines PA, LNA, and switch
mmTron announced its first single-chip front-end IC for mmWave communications. Covering 24 to 30 GHz, the TMC252 integrates a power amplifier (PA), low noise amplifier (LNA), and transmit-receive switch on a single GaN IC that is available as a die or packaged in a 5 mm x 5 mm air-cavity QFN. The TMC252 is well-suited…
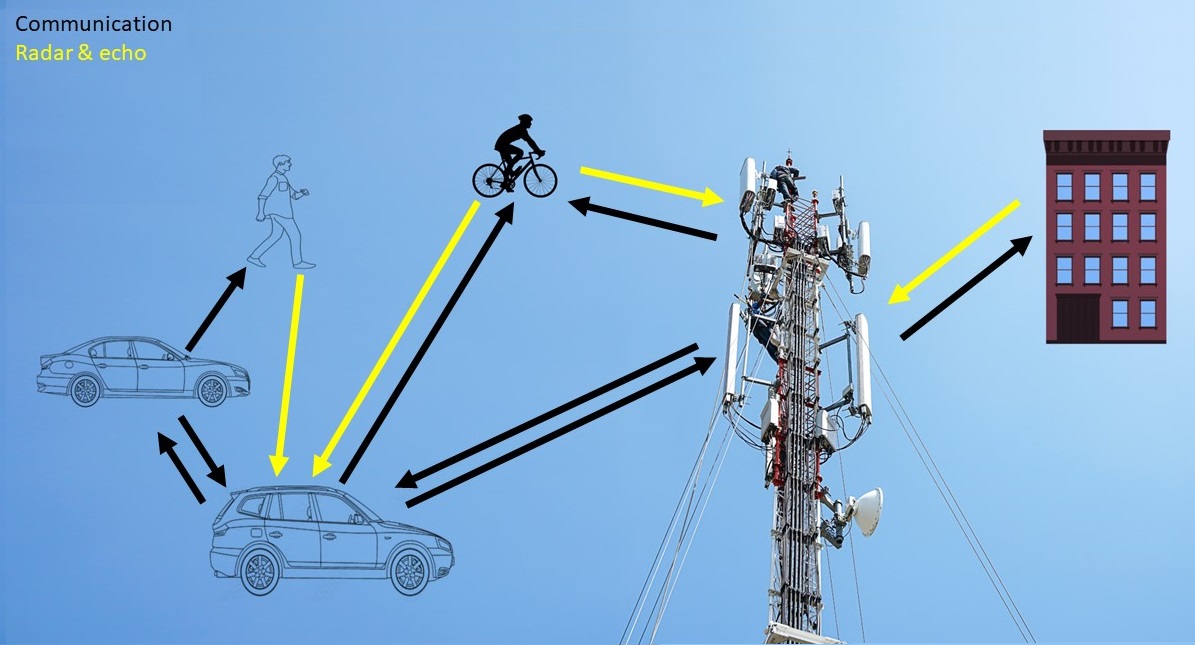
6G could add sensing to cellular networks
Integrated communications and sensing at mmWave and sub-THz frequencies could add location detection that helps avoid accidents among pedestrians, bicycles, and vehicles.
Report models performance of reconfigurable intelligent surfaces
ETSI unveils a new Report developed by its Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces group. ETSI GR RIS-003 explores communication models that offer a trade-off between electromagnetic accuracy and simplicity for performance evaluation and optimization. It also analyses channel models that include path-loss and multipath propagation effects, as well as the impact of interference. The last part of…
EE World’s 2023 communications handbook is here
Our 2023 5G, Wired, & Wireless Handbook is now available in ebook form. Download your copy today. It started on a cold January day with an editorial call. A month later, the abstracts came in. After another month, the manuscripts came in. Then came the editing and some back-and-forth with the authors. Next, it was…
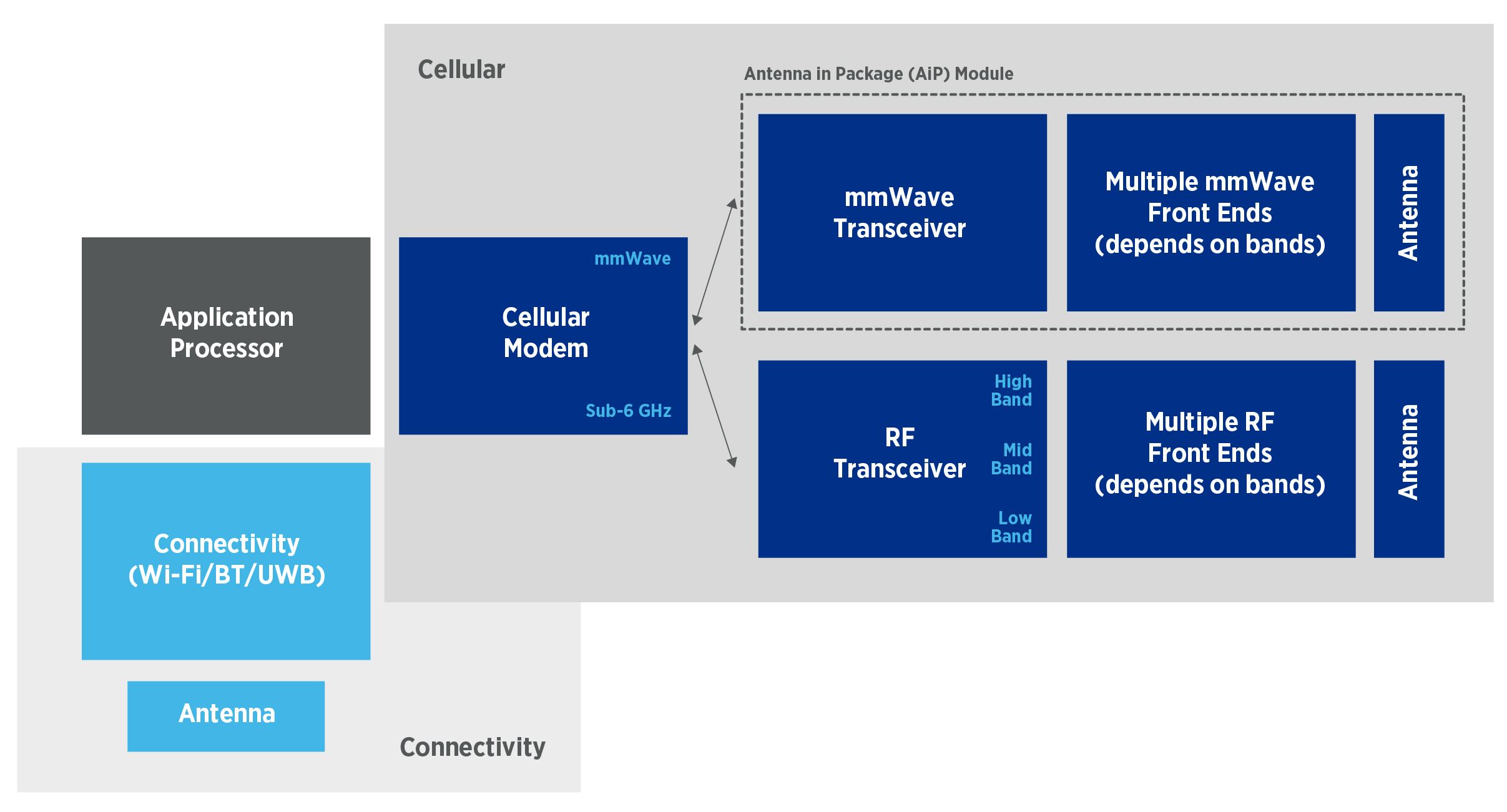
5G mmWave test builds on RF best practices
The high level of integration in today’s mmWave phone means traditional test methods no longer apply.
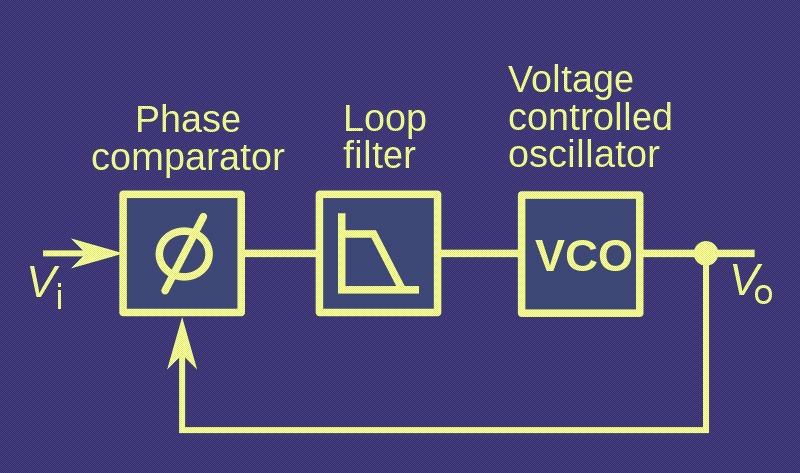
5G mmWave signal chain: the phase-locked loop
In “Look inside the 5G mmWave signal chain,” we explored the overall architecture of the mmWave signal chain. Now, we’ll look deeper into each of a transceiver’s components. Phase-locked Loops (PLL) are important blocks for a clean reference clock generation in cellular networks. In 5G mmWave radio networks, the PLL supports data rates of 1…
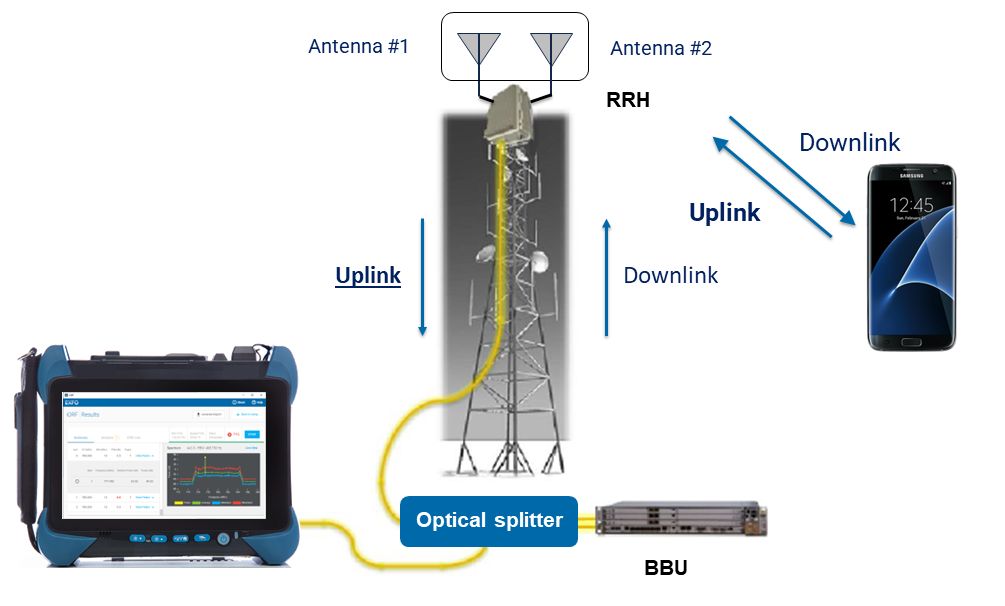
Identify, troubleshoot, and resolve PIM issues in wireless networks
5G brought passive intermodulation problems into the spotlight. Now it’s up to engineers and technicians to identify and mitigate signal degradation to minimize dropped calls and other issues. A loose connection; a metal roof; power lines. Even a rusty bolt. It’s estimated that mobile operators will spend $1.1 trillion on capital expenditure between 2020 and…
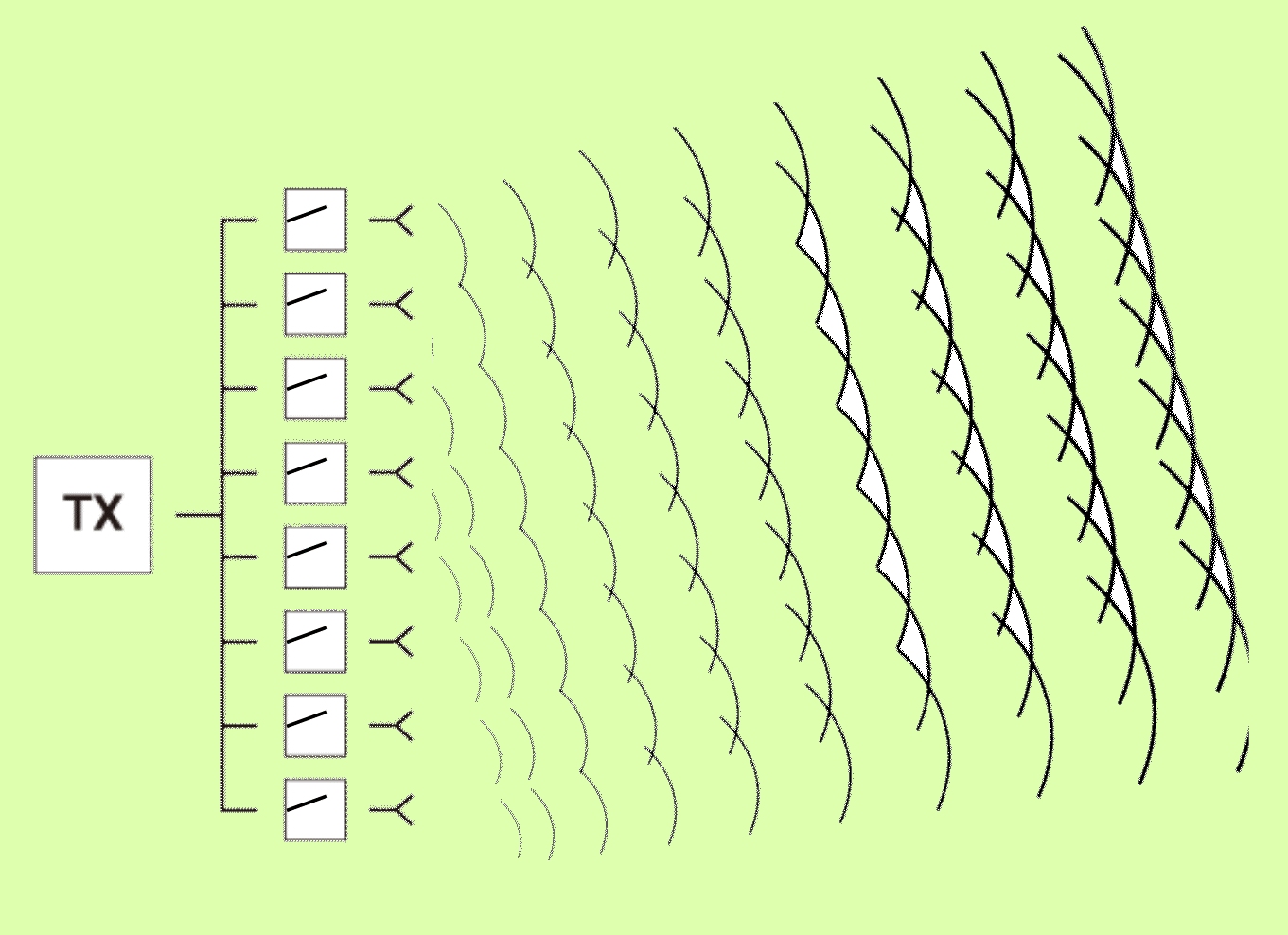
Test methods for mmWave AiP designs bring tradeoffs
Engineers have several mmWave over-the-air test methods available for evaluating phased-array antennas used in antenna-in-package designs. Each has pros and cons.