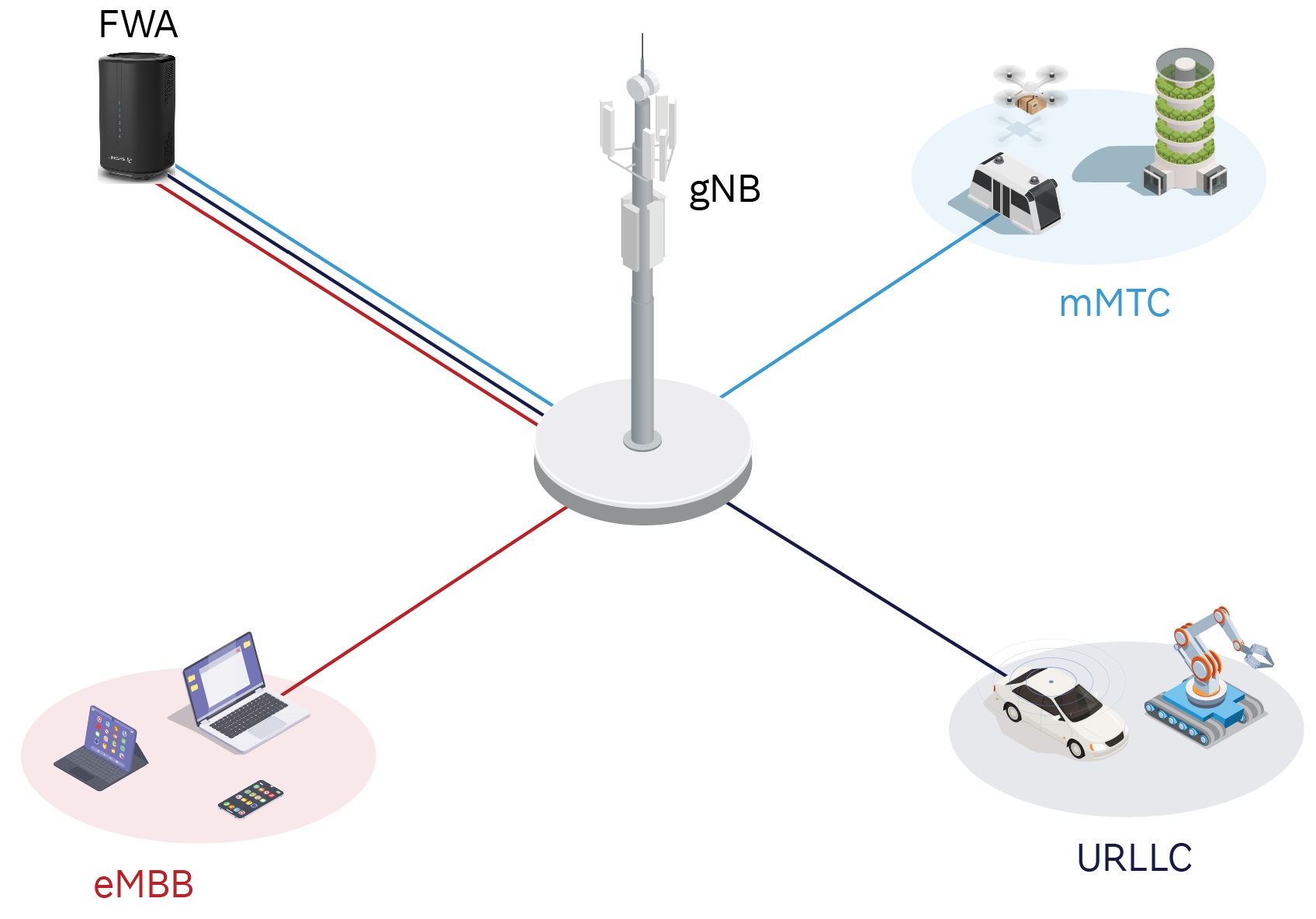
Fixed-wireless access is a special use case of enhanced mobile broadband, one of the three use cases specified for 5G. FWA brings different challenges for deployment than eMBB.
OFC 2024: It’s AI or die
Today’s data rates are already too slow, and so are tomorrow’s. Expect more complaints about slow networks in 2025.
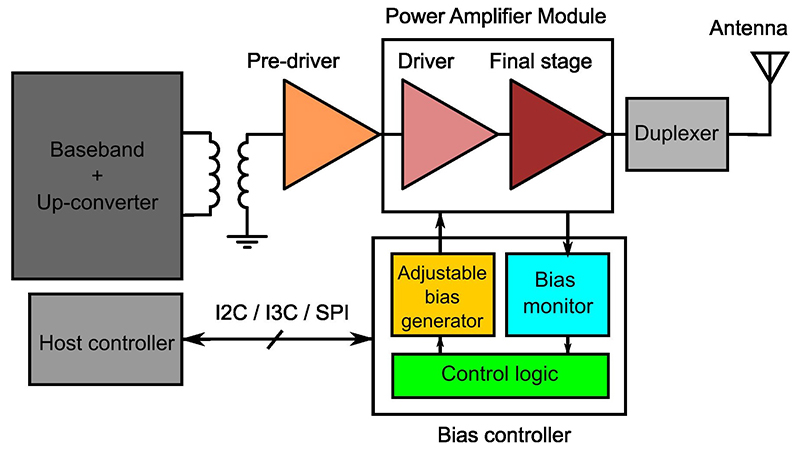
Choose a 5G base station’s PA bias control circuit
Bias control of PAs is crucial to ensure optimum radio performance under all conditions. Current sensing and temperature sensing provide the feedback needed to control the PA bias. The choice of sensing and biasing circuits brings design trade-offs. 5G base station power amplifiers (PAs) need biasing using a separate bias controller to maintain optimum performance…
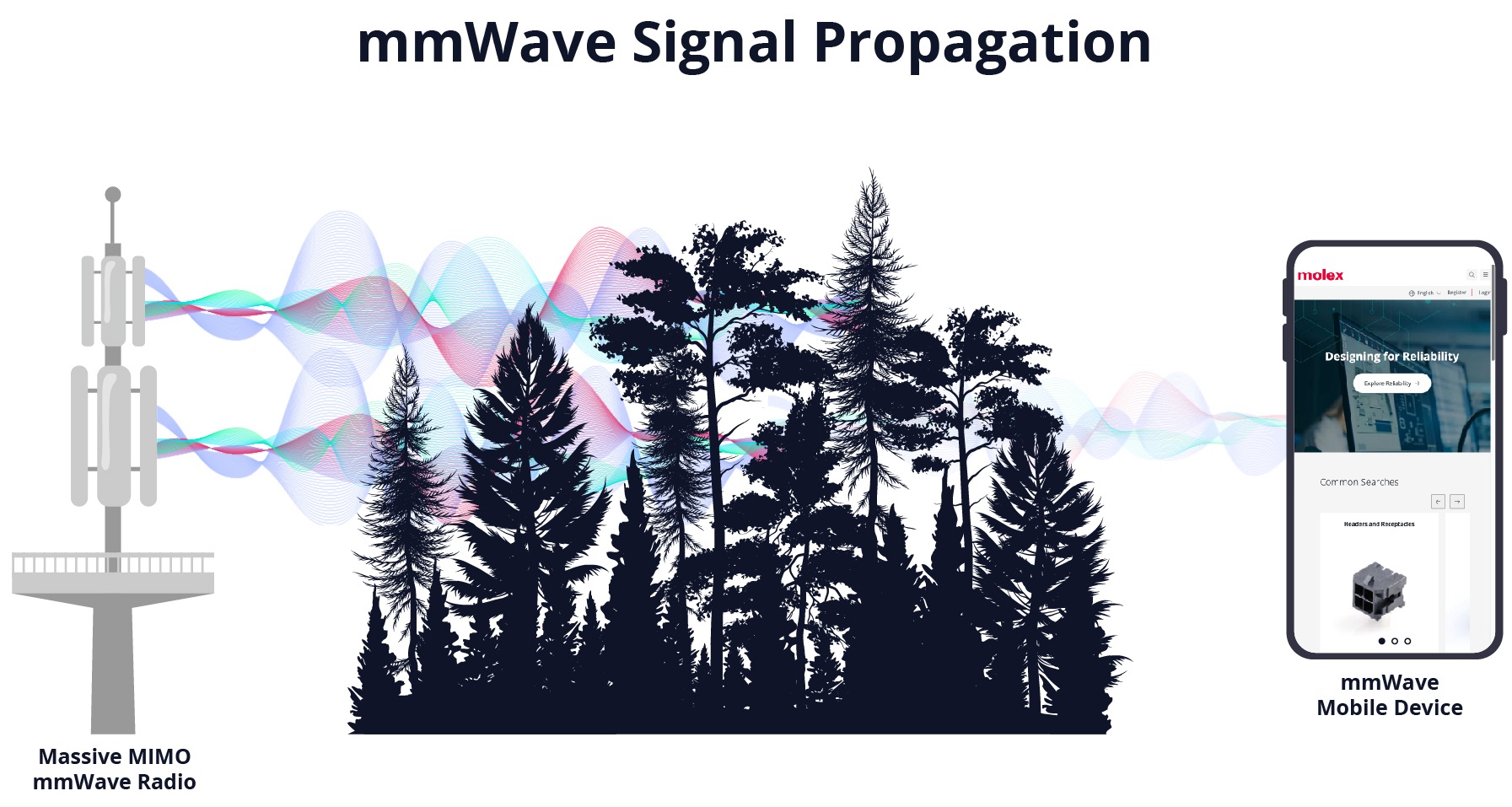
mmWaves bring interconnect challenges to 5G and 6G
Signals in the mmWave range require extra care and more expensive components than at sub-6 GHz frequencies.
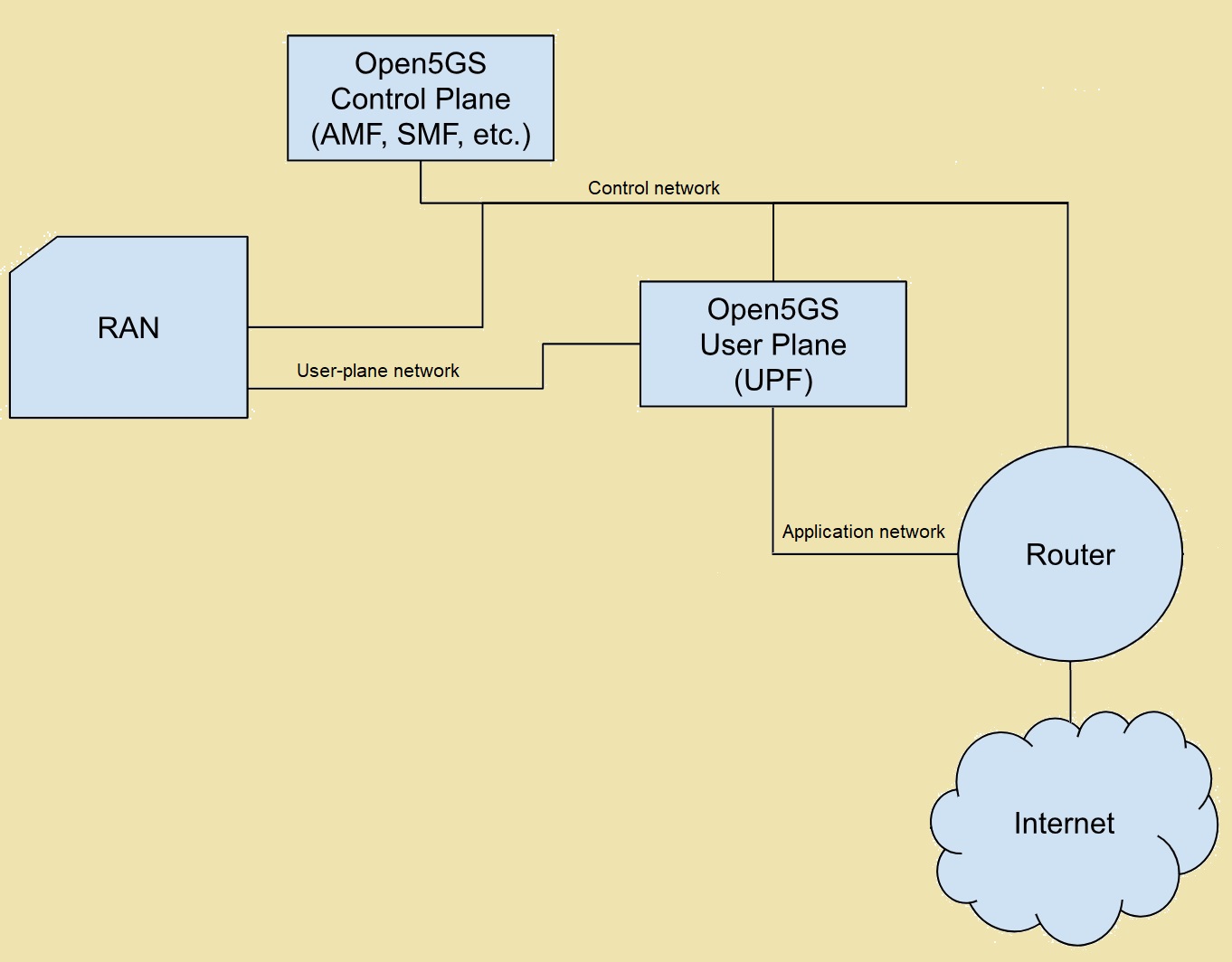
Build a 5G Open RAN test lab with open-source software tools
Open-source software provides network components that you can use to simulate 5G network functions from the network core to the radio. Developing and deploying a laboratory infrastructure to support testing 5G and open radio-access network (Open RAN) systems can present a daunting and complex task. Prior to Open RAN, this task was only possible by…
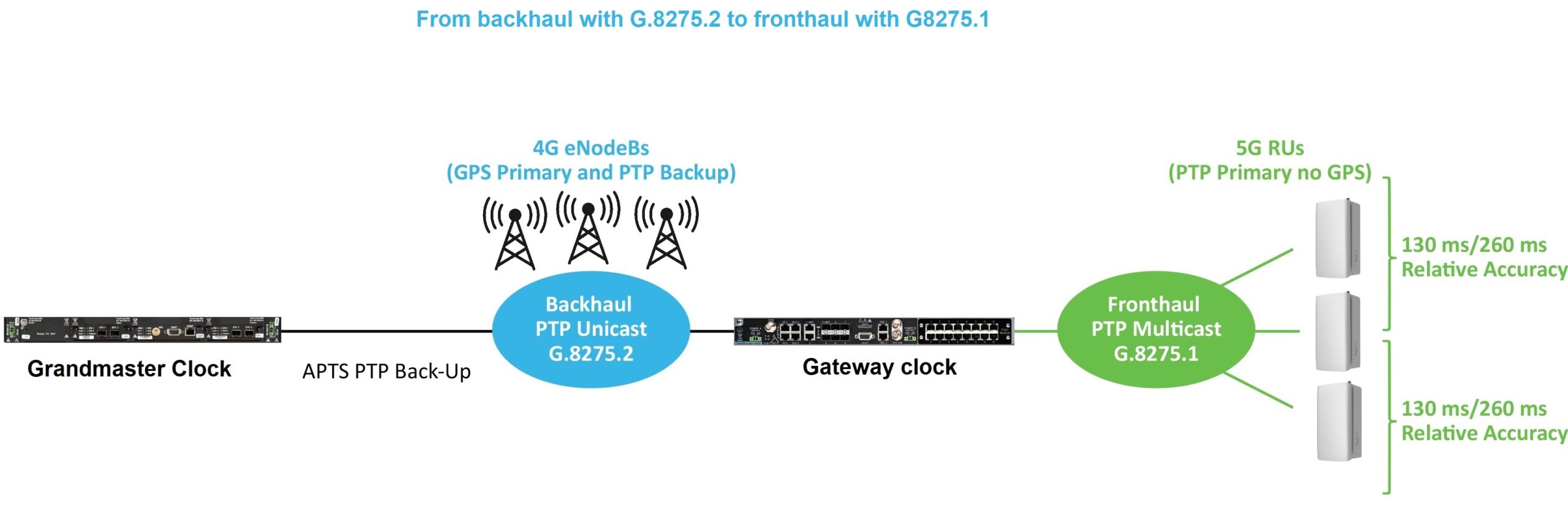
Flexible PTP profiles ease the transition to 5G
5G brought architecture changes that require synchronization. Depending on the location and network site, those timing requirements require different PTP profiles and PTP capacity.
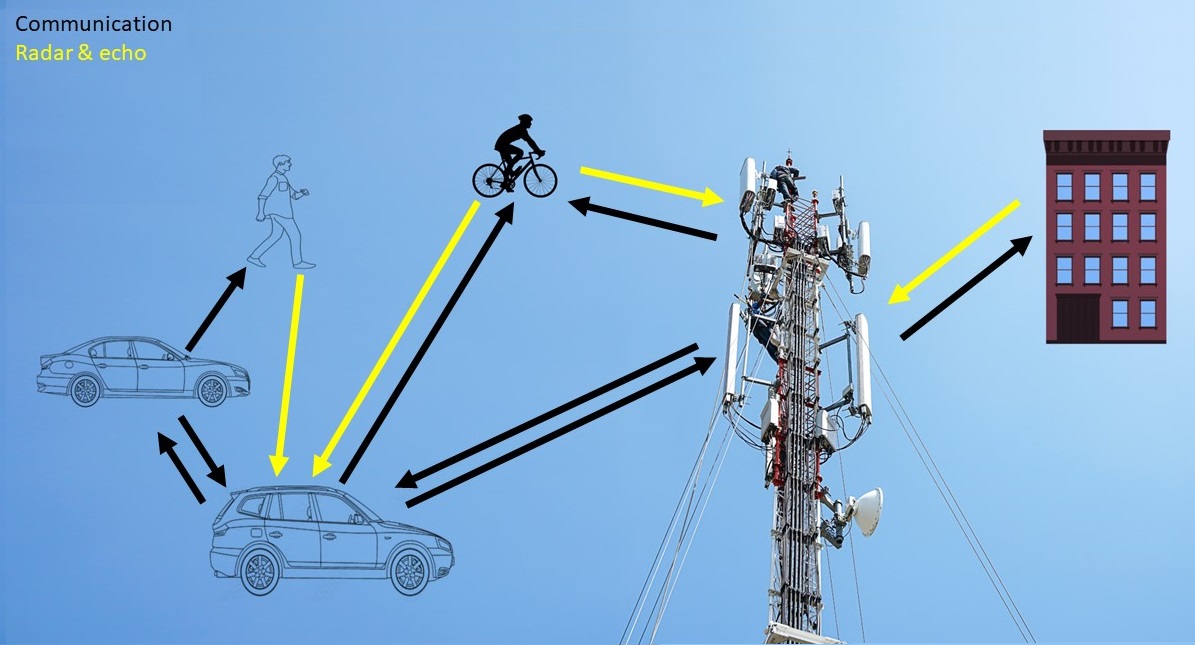
6G could add sensing to cellular networks
Integrated communications and sensing at mmWave and sub-THz frequencies could add location detection that helps avoid accidents among pedestrians, bicycles, and vehicles.
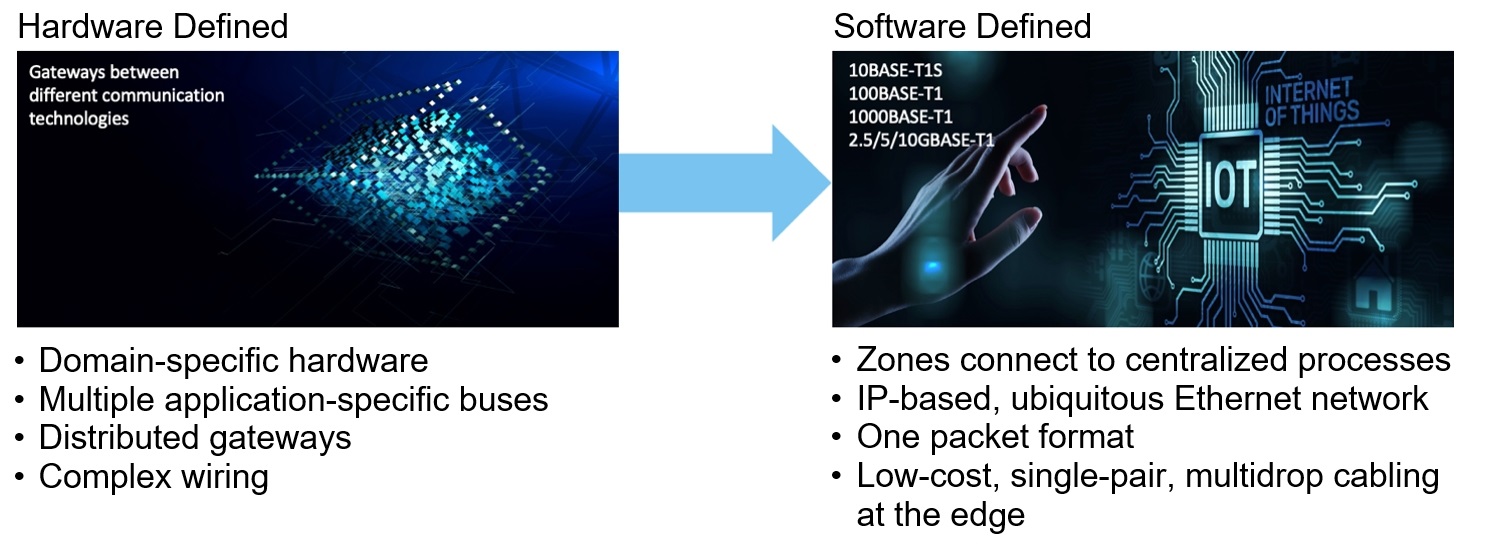
10BASE-T1S brings a single pair of wires to the network edge
The 802.3cg Ethernet standard uses a single pair of wires, and it manages data flow without switches, making it suitable for industrial networks at a lower cost than traditional Ethernet. Industrial plants have long used digital data to monitor and control their production facilities. Networks in factories, data centers, and commercial buildings push the edges…
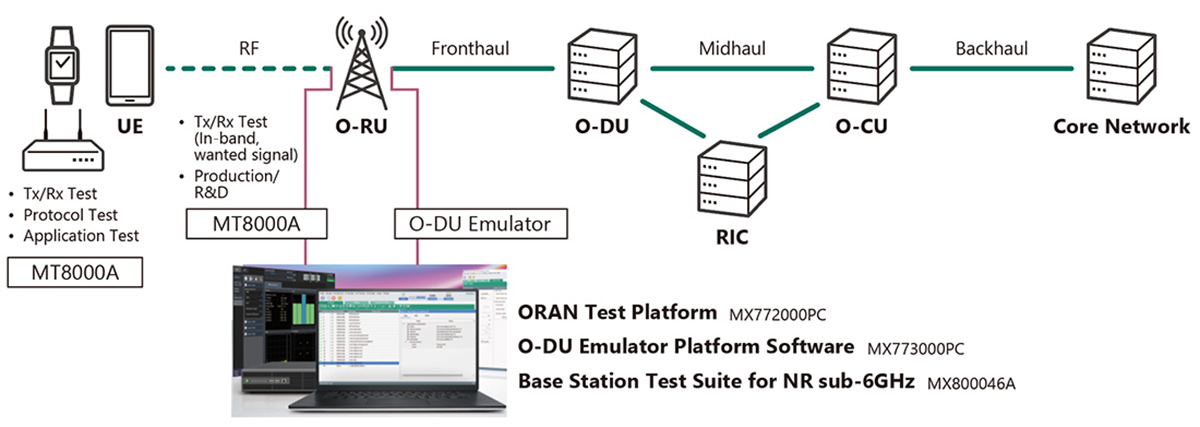
How do you test an Open RAN installation?
Open RAN telecom networks need testing for each disaggregated component, but that’s not enough. End-to-end testing is also necessary. In How do Open RAN interfaces work?, we covered how Open RAN redefines traditional RAN architecture by disaggregating it into three primary components: the radio unit (RU), distributed unit (DU), and centralized unit (CU). This paradigm…
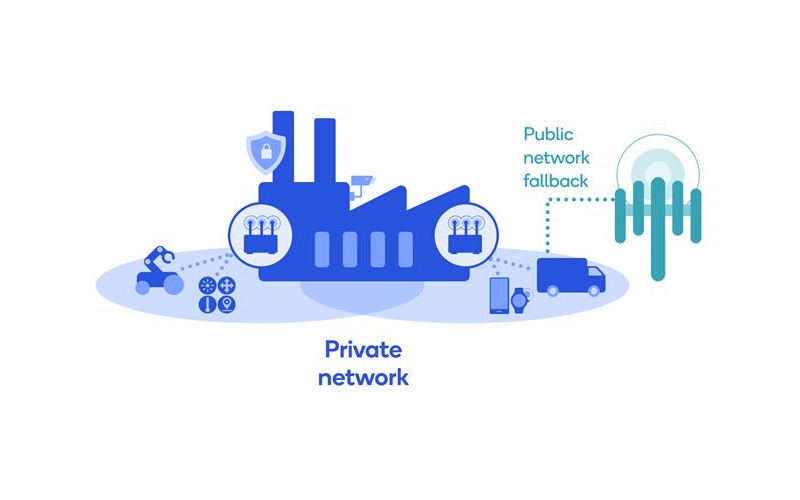
What is a private 5G network? How does it work?
Private networks have the potential to change many industries and become the primary application for 5G. Processes and protocols make them work.