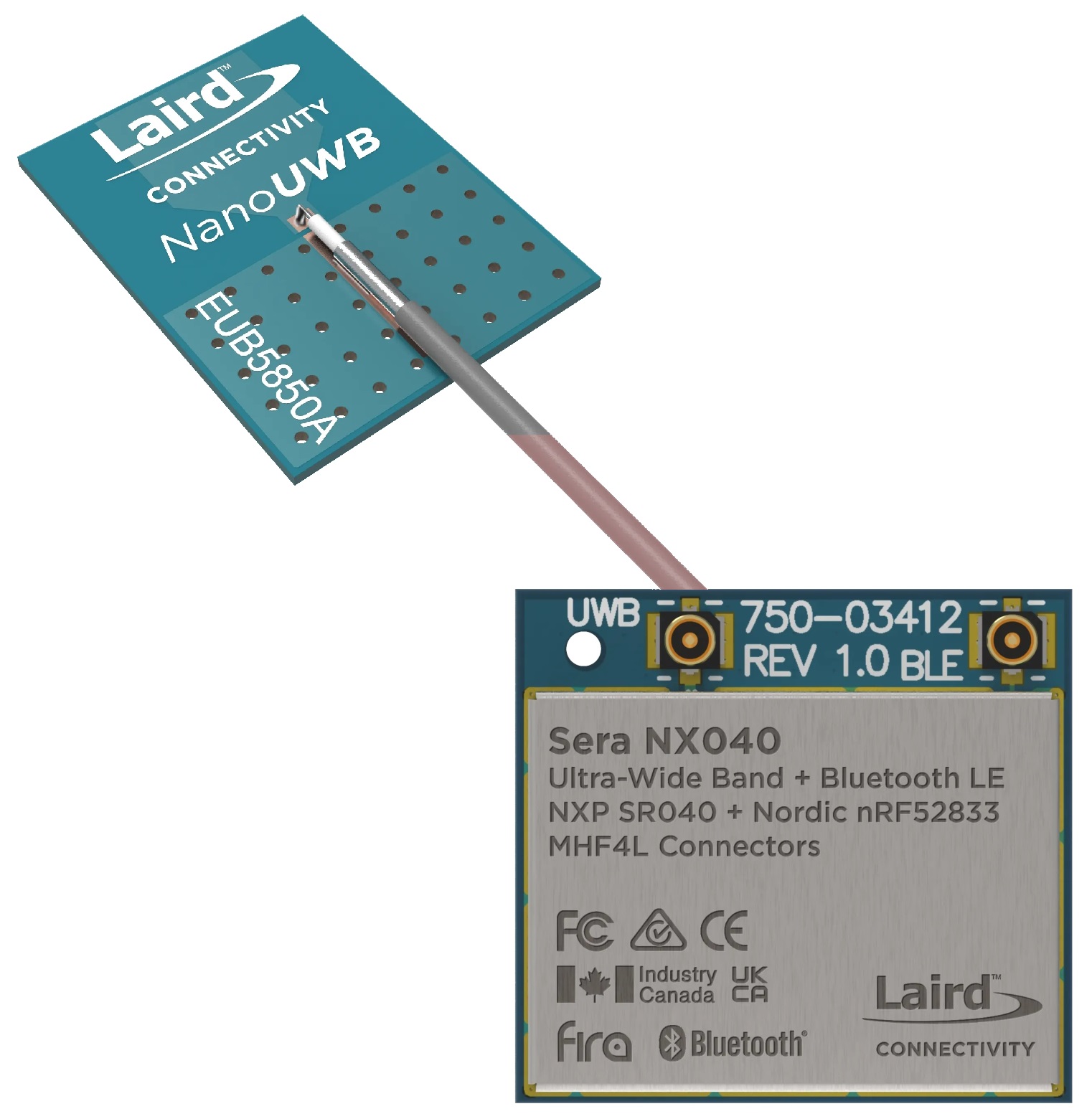
The NanoUWB planar monopole antenna from Laird Connectivity adds UWB to consumer and IoT devices that need precise location data.
UWB applications bring design decisions
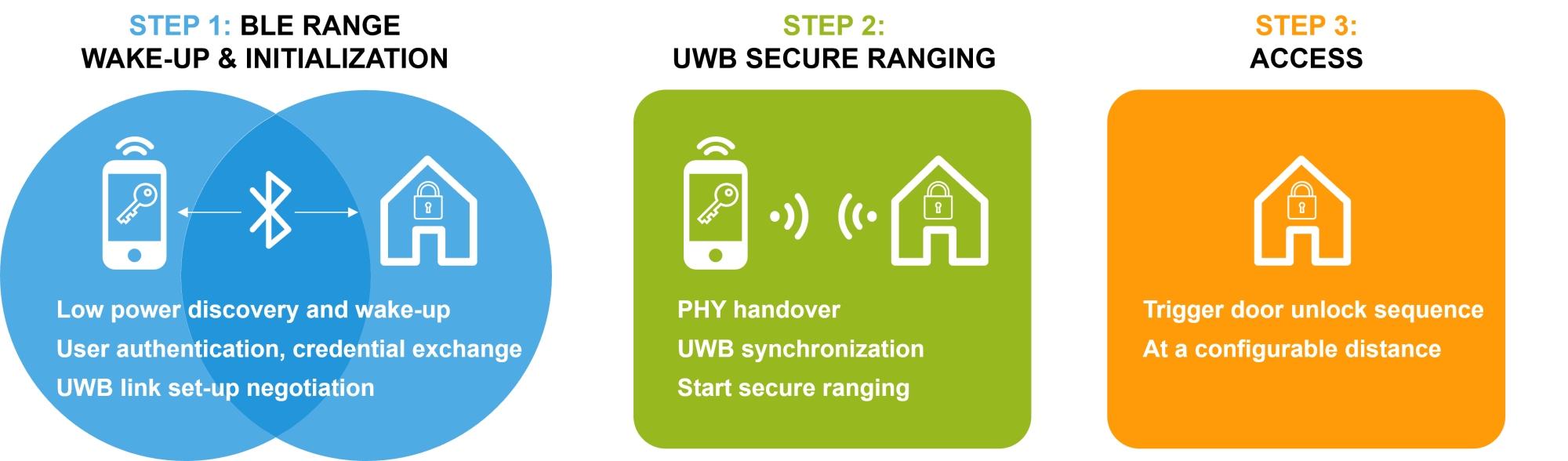
Ultra-wideband communications and location detection applications are steadily increasing. As a designer, you have options and therefore must decide how to best integrate UWB into your IoT design. Impulse radio ultra-wideband, commonly referred to as UWB, is a short-range, wireless communication protocol based on the IEEE 802.15.4z standard, operating at frequencies up to 9.5 GHz.…
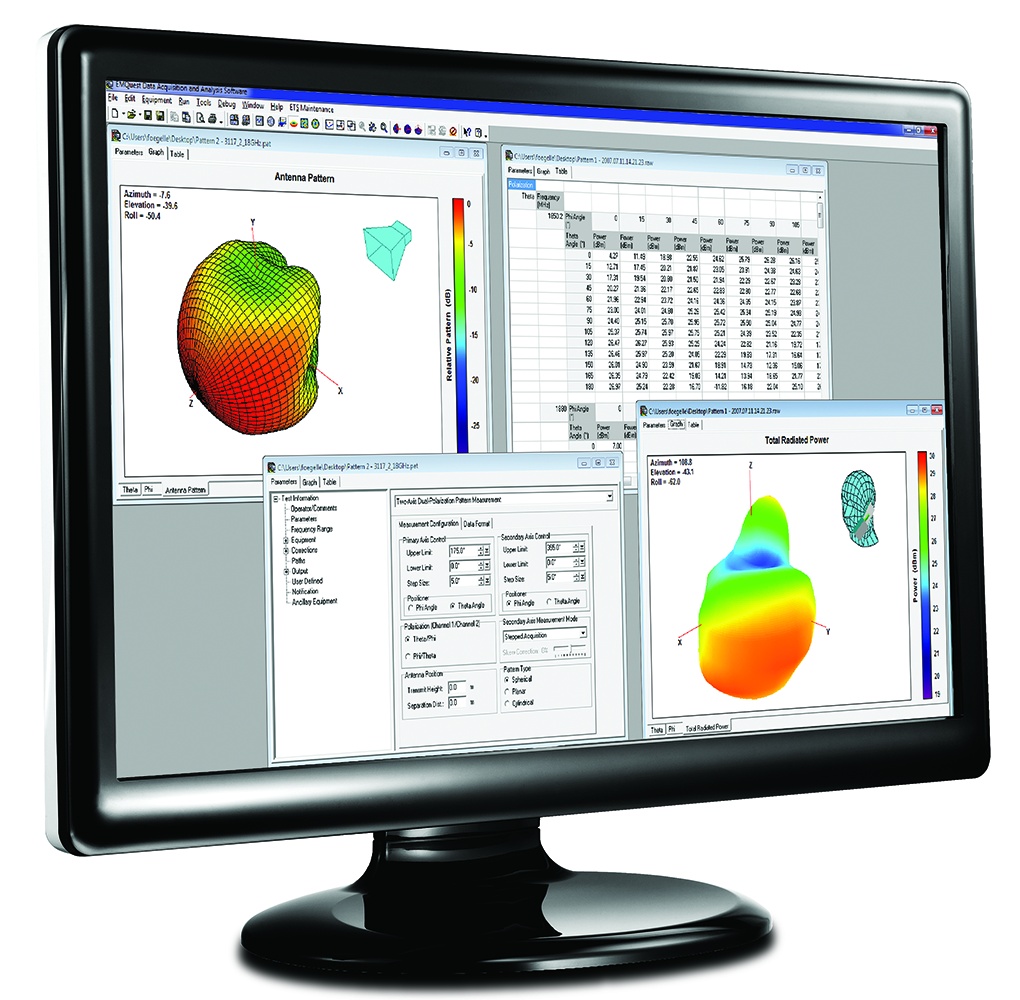
OTA wireless test system supports Wi-Fi 6 and 6E
ETS-Lindgren’s EMQuest software now supports the most current versions of Wi-Fi while maintaining backward compatibility.
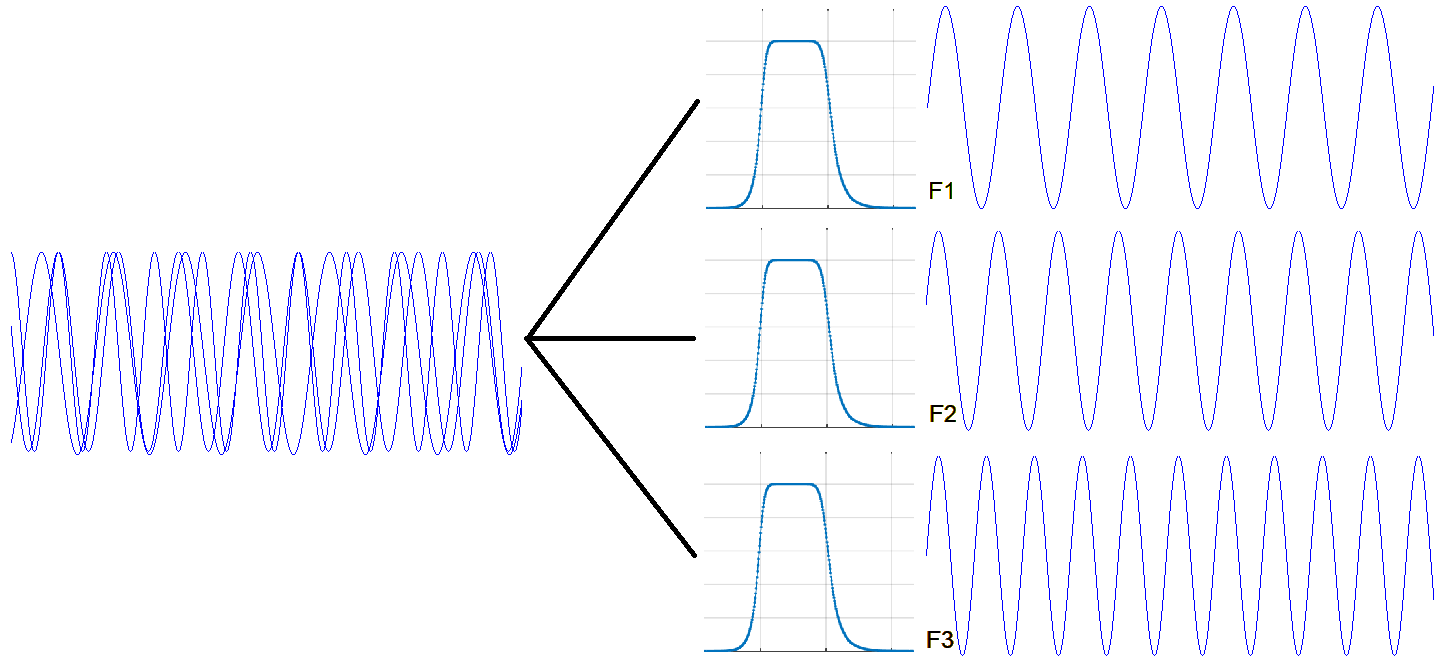
Filters keep RF signals in line
In a video interview with 5G Technology World, Resonant’s Mike Eddy explains how RF filters keep wanted signals in an interference out. It’s all in the physics. As bandwidth gets crowded, governments auction more spectrum to accommodate our insatiable demand for data. While 3G used frequencies around 1 GHz, 4G expanded to around 2 GHz.…
Add UWB hardware and software to IC designs
CEVA’s Riviera Waves IP lets you add an Ultra-Wideband digital PHY and hardware/software MAC layer to an IC design for use in low-power devices.