5G Technology World spoke with Moshe Sheier and Nir Shapira of CEVA to learn how the company’s DSP core handles 5G baseband signals from I/O data to the transport network.
On April 30, Silicon Valley based CEVA announced that Picocom had licensed CEVA’s digital-signal processing (DSP) IP for use in ICs that go into 5G small cells. DSP plays a crucial role in the 5G signal chain and CEVA provides the DSP architecture to handle baseband signal processing.
After a 5G RF/mmWave signal is converted to baseband, the DSP takes over, processing the signal from I/Q bits to a form suitable for network transport. In effect, the DSP forms a software-defined radio used in network and user wireless equipment.
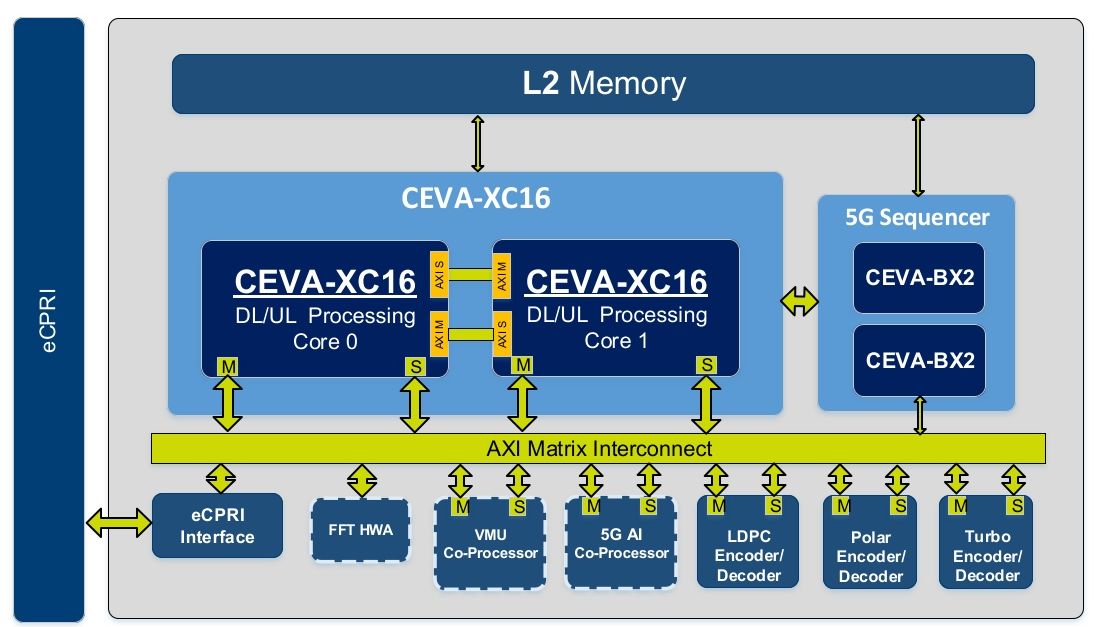 As CEVA’s Nir Shapira explains in the video, the DSP core can process data from the I/Q bits on the receive side into a form that’s ready for transport. On the transmit side, the DSP processes incoming bits and gets them ready to send to the RF circuits. Users can customize the signal chain for specific use cases. The figure below shows an application of DSP in the signal chain.
As CEVA’s Nir Shapira explains in the video, the DSP core can process data from the I/Q bits on the receive side into a form that’s ready for transport. On the transmit side, the DSP processes incoming bits and gets them ready to send to the RF circuits. Users can customize the signal chain for specific use cases. The figure below shows an application of DSP in the signal chain.
Of course, the baseband DSP is just one of the functions needed in a complete signal chain. 5G Technology World will soon look at other aspects of 5G where engineers use licensed IP as building blocks.


Tell Us What You Think!