The QPB9378 from Qorvo covers 5G’s mid-band, seen as the sweet spot for range and bandwidth.
5G’s mid-band frequencies, which include those aimed at CBRS and private networks, combine reasonable range and penetration along with bandwidth. Qorvo’s QPB9378 dual low-noise amplifier (LNA) covers 2.3 GHz to 5 GHz, a range that covers T-Mobile at the low end and Verizon/AT&T at the higher end, including the controversial C-band (3.7 GHz to 3.98 GHz) frequencies near the 4.2 GHz to 4.4 GHz frequencies used by aircraft altimeters. The QPB9378 covers all those frequencies — 5G bands n40, n41, n78, n79. LTE- b40, b41, b42, b43 — up to the edge of 5 GHz Wi-Fi.
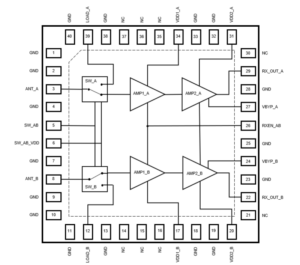
In transmit mode, the QPB9378 can produce 20 W of power. As a receiver, it adds 33.5 dB of signal gain (high gain state) or 14.5 dB in low-gain state. The low-gain state comes from bypassing the second-stage amplifier of each channel (see functional block diagram).
The LNA adds 0.5 dB of insertion loss to the signal chain with a 1.25 dB (1.6 dB max) noise figure. Power supply voltage range is 4.75 V to 5.25 V. The QPB9378 comes packaged in a 6 mm×6 mm package.
Applications include 5G mMIMO, small cells, and time-division duplex (TDD)-based radio architectures. Qorvo offers two evaluation board versions: 2.3 GHz to 4.2 GHz and 4.4 GHz to 5 GHz, avoiding the aircraft altimeter frequencies.



Tell Us What You Think!