(Image Credit: ESA/NASA/JPL/ASI/Univ. Rome; R. Orosei et al 2018)
ESA’s Mars Express radar team recently made an exciting announcement: data from their instrument points to a pond of liquid water buried about 1.5 km below the icy south polar ice of Mars.
Between 2012 and 2015 Mars Express made repeated passes over the 200 km wide study region in Planum Australe, bouncing radio waves through the planet’s surface and recording the properties of the reflected signal with its Mars Advanced Radar for Subsurface and Ionosphere Sounding instrument, MARSIS.
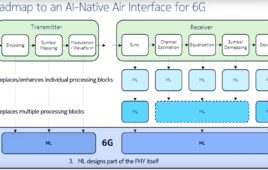
The radar ‘footprints’ on the surface are represented in the image and are colour-coded corresponding to the ‘power’ of the signal reflected from features below the surface. The brightest reflections are coloured in blue, with data from multiple overlapping orbits defining a 20 km-wide zone corresponding to the triangular shaped patch to the right of centre in this image.
Directly below this patch, under repeating layers of ice and dust at a depth of 1.5 km, is a base layer that has radar properties corresponding to liquid water. Despite the below-freezing temperatures on Mars, it can be kept liquid by the presence of salts, and it may be heavily laden with water-saturated sediments.
Water once flowed freely on the Red Planet’s surface, but it is not stable today. Discovering liquid water buried underground is essential for understanding the evolution of Mars, the history of water on our neighbour planet, and its habitability.