Physicists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and partners have demonstrated an experimental, next-generation atomic clock–ticking at high “optical” frequencies–that is much smaller than usual, made of just three small chips plus supporting electronics and optics.
Described in Optica, the chip-scale clock is based on the vibrations, or “ticks,” of rubidium atoms confined in a tiny glass container, called a vapor cell, on a chip. Two frequency combs on chips act like gears to link the atoms’ high-frequency optical ticks to a lower, widely used microwave frequency that can be used in applications.
The chip-based heart of the new clock requires very little power (just 275 milliwatts) and, with additional technology advances, could potentially be made small enough to be handheld. Chip-scale optical clocks like this could eventually replace traditional oscillators in applications such as navigation systems and telecommunications networks and serve as backup clocks on satellites.
“We made an optical atomic clock in which all key components are microfabricated and work together to produce an exceptionally stable output,” NIST Fellow John Kitching said. “Ultimately, we expect this work to lead to small, low-power clocks that are exceptionally stable and will bring a new generation of accurate timing to portable, battery-operated devices.”
The clock was built at NIST with help from the California Institute of Technology (Pasadena, Calif.), Stanford University (Stanford, Calif.) and Charles Stark Draper Laboratories (Cambridge, Mass.).
Standard atomic clocks operate at microwave frequencies, based on the natural vibrations of the cesium atom–the world’s primary definition of the second. Optical atomic clocks, running at higher frequencies, offer greater precision because they divide time into smaller units and have a high “quality factor,” which reflects how long the atoms can tick on their own, without outside help. Optical clocks are expected to be the basis for a future redefinition of the second.
In NIST’s original chip-scale atomic clock, the atoms were probed with a microwave frequency. Commercial versions of this clock have become an industry standard for portable applications requiring high timing stability. But they require initial calibration and their frequency can drift over time, resulting in significant timing errors.
Compact optical clocks are a possible step up. Until now, optical clocks have been bulky and complex, operated only as experiments by metrological institutions and universities.
Optical ticks in rubidium have been studied extensively for use as frequency standards and are accurate enough to be used as length standards. NIST’s rubidium vapor cell and the two frequency combs are microfabricated in the same way as computer chips. This means they could support further integration of electronics and optics and could be mass produced–a path toward commercially viable, compact optical clocks.
NIST’s chip-based optical clock has an instability of 1.7 x 10?13 at 4,000 seconds–about 100 times better than the chip-scale microwave clock.
The clock works like this: The rubidium atoms’ tick at an optical frequency in the terahertz (THz) band. This ticking is used to stabilize an infrared laser, called a clock laser, which is converted to a gigahertz (GHz) microwave clock signal by two frequency combs acting like gears. One comb, operating at a THz frequency, spans a broad enough range to stabilize itself. The THz comb is synchronized with a GHz frequency comb, which is used as a finely spaced ruler locked to the clock laser. The clock thus produces a GHz microwave electrical signal–which can be measured by conventional electronics–that is stabilized to the rubidium’s THz vibrations.
In the future, the chip-based clock’s stability may be improved with low-noise lasers and its size reduced with more sophisticated optical and electronic integration.
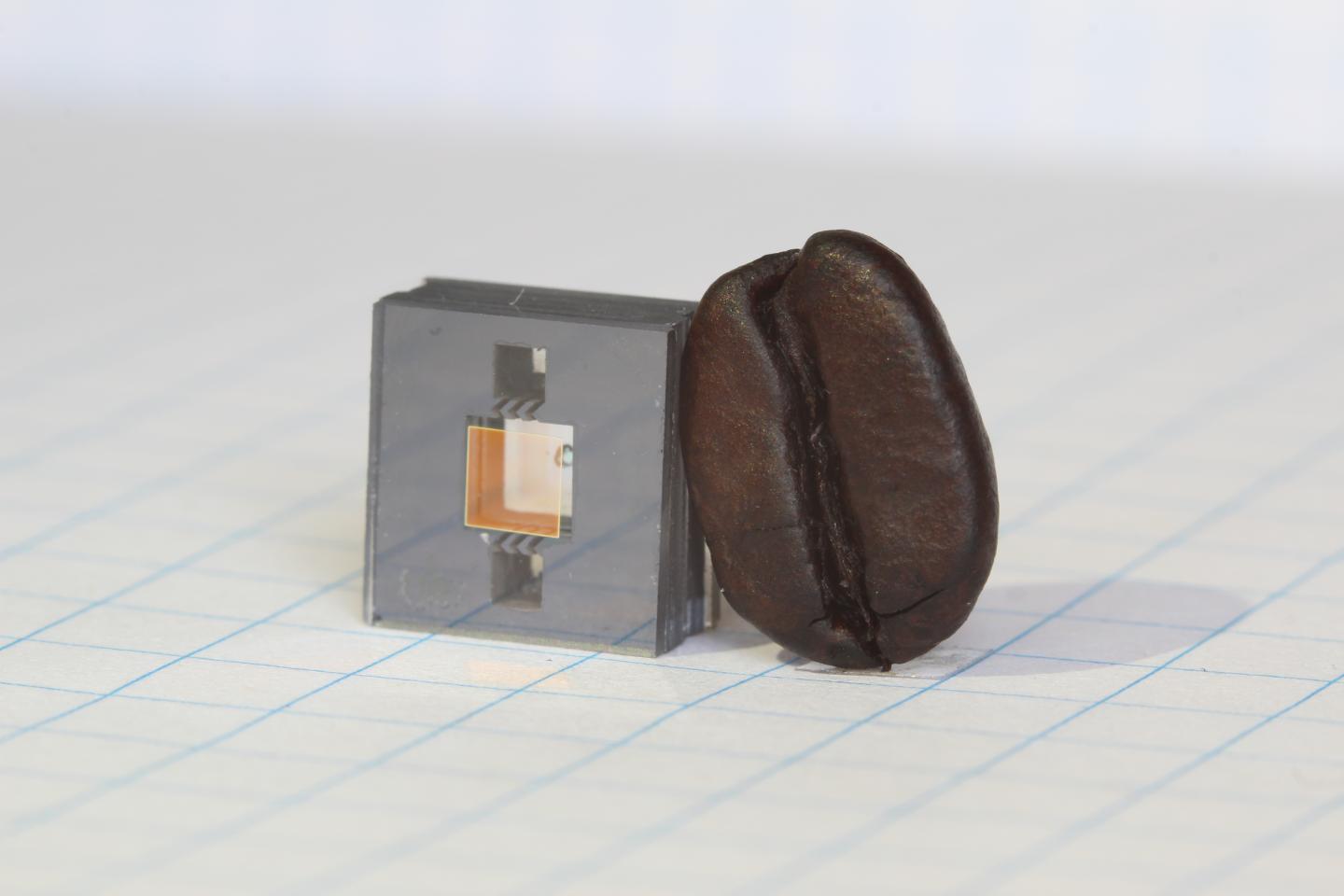
Physicists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and partners have demonstrated an experimental, next-generation atomic clock–ticking at high “optical” frequencies–that is much smaller than usual, made of just three small chips plus supporting electronics and optics. (Image Source: Hummon/NIST)