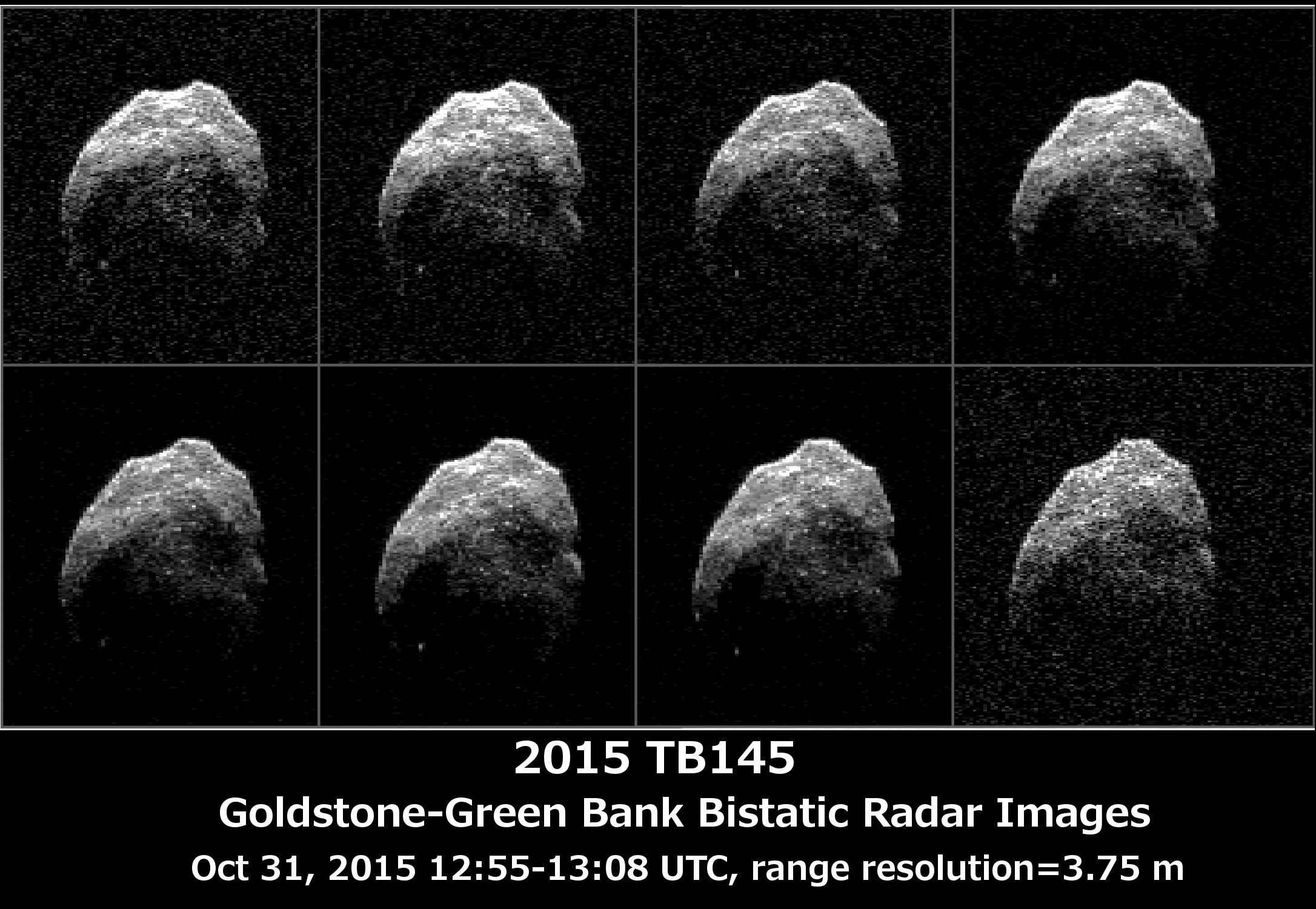
Asteroid 2015 TB145 is depicted in eight individual radar images collected on Oct. 31, 2015 between 5:55 a.m. PDT (8:55 a.m. EDT) and 6:08 a.m. PDT (9:08 a.m. EDT). At the time the radar images were taken, the asteroid was between 440,000 miles (710,000 kilometers) and about 430,000 miles (690,000 kilometers) distant. Asteroid 2015 TB145 safely flew past Earth on Oct. 31, at 10:00 a.m. PDT (1 p.m. EDT) at about 1.3 lunar distances (300,000 miles, 480,000 kilometers). To obtain the radar images, the scientists used the 230-foot (70-meter) DSS-14 antenna at Goldstone, California, to transmit high power microwaves toward the asteroid. The signal bounced of the asteroid, and their radar echoes were received by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory’s 100-meter (330-foot) Green Bank Telescope in West Virginia. The images achieve a spatial resolution of about 13 feet (4 meters) per pixel. (Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/GSSR/NRAO/GB)
The highest-resolution radar images of asteroid 2015 TB145’s safe flyby of Earth have been processed and yield new information about its surface features.
To obtain these highest-resolution radar images of the asteroid, scientists used the 230-foot (70-meter) DSS-14 antenna at Goldstone, California, to transmit high-power microwaves toward the asteroid. The signal bounced off the asteroid, and its radar echoes were received by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory’s (NRAO) 100-meter (330-foot) Green Bank Telescope in West Virginia. The radar images achieve a spatial resolution as fine as 13 feet (4 meters) per pixel.
The radar images were taken as the asteroid flew past Earth on October 31 at 1 p.m. EDT at about 1.3 lunar distances (300,000 miles, or 480,000 kilometers) from Earth. Asteroid 2015 TB145 is spherical in shape and approximately 2,000 feet (600 meters) in diameter.
“The radar images of asteroid 2015 TB145 show portions of the surface not seen previously and reveal pronounced concavities, bright spots that might be boulders, and other complex features that could be ridges,” said Lance Benner of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, who leads NASA’s asteroid radar research program. “The images look distinctly different from the Arecibo radar images obtained on October 30 and are probably the result of seeing the asteroid from a different perspective in its three-hour rotation period.”
“Working with our observatory partners, we were able to get our resolution down to less than 13 feet (four meters) per pixel,” said Shantanu Naidu, a postdoctoral student at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, and a member of the radar team. “It is a truly remarkable achievement, one which we will later be able to apply when future flyby opportunities present themselves.”
The next time that asteroid 2015 TB145 will be in Earth’s neighborhood will be in September 2018, when it will make a distant pass at about 24 million miles (38 million kilometers), or about a quarter the distance between Earth and Sun.
Radar is a powerful technique for studying an asteroid’s size, shape, rotation, surface features and surface roughness, and for improving the calculation of asteroid orbits. Radar measurements of asteroid distances and velocities often enable computation of asteroid orbits much further into the future than would be possible otherwise.
The 100-meter GBT is the world’s largest fully steerable radio telescope. Its location in the National Radio Quiet Zone and the West Virginia Radio Astronomy Zone protects the incredibly sensitive telescope from unwanted radio interference, enabling it to perform unique observations.