The PC802 PHY SoC from Picocom connects RFICs to access networks.
5G’s promise of significantly greater bandwidth and data rates needs mmWave signals. Because of mmWave’s short distances, telecom operators need many small cells, which engineers design. A crucial part of the signal chain is the 5G PHY, which takes IQ data from a transceiver and interfaces it to a digital link, usually Ethernet. The PHY generally has two parts, called a low PHY and high PHY. The PC802 PHY SoC from Picocom handles both parts of the 5G PHY.
The PC802 supports the FR1 and FR2 5G NR frequency bands as well as supporting LTE, a fallback for locations where 5G isn’t available. The block diagram in Figure 1 shows the quad FESD204B serial interface between the PHY and an RFIC.
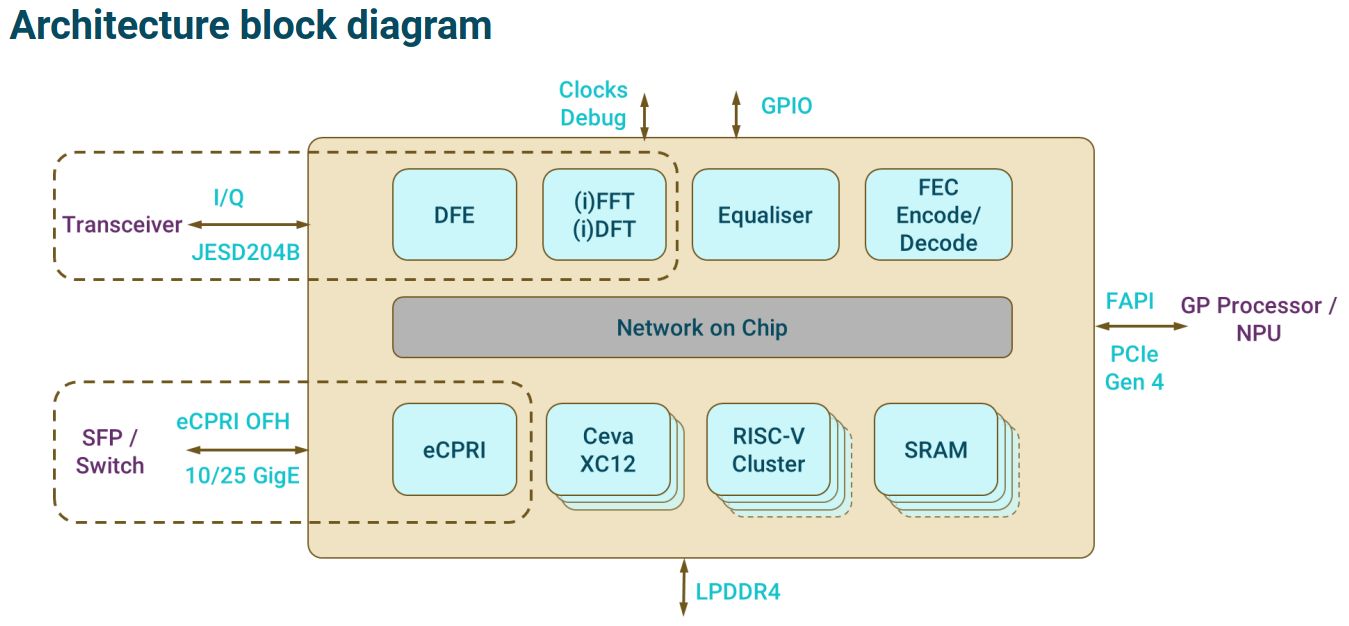
Figure 1. The PC802 PHY SoC provides an interface between RFIC (mmwave and sub 6 GHz) and radio access networks.
On the network side, the PC802 supports functional splits — the separation of low and high PHY functions — into splits 2 and 6 for disaggregated radio access networks (RANs) and the 7.2 split for Open RAN. Figure 2 shows the options for functional splits.
 When operating at sub-6 GHz, the PC802 supports 8 Tx and 8 Rx baseband ports with 100 MHz bandwidth. At mmWave FR2, it supports 2 Tx/2 Rx with 100 MHz bandwidth. The silicon runs Picocom’s 5G NR and LTE PHY software on a CEVA 1280-bit vector signal processor.
When operating at sub-6 GHz, the PC802 supports 8 Tx and 8 Rx baseband ports with 100 MHz bandwidth. At mmWave FR2, it supports 2 Tx/2 Rx with 100 MHz bandwidth. The silicon runs Picocom’s 5G NR and LTE PHY software on a CEVA 1280-bit vector signal processor.
Applications for the PC802 include indoor residential and enterprise private networks. It also supports outdoor network small cells.


Tell Us What You Think!