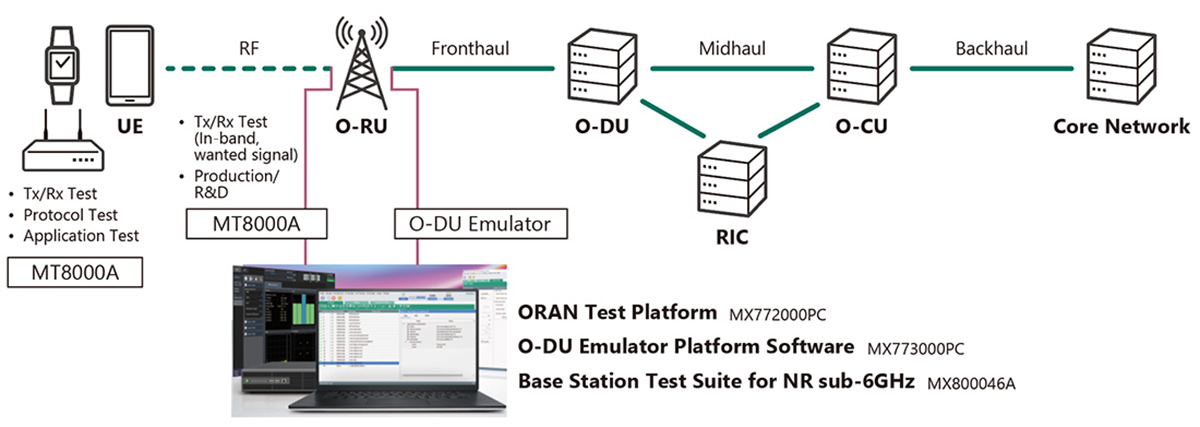
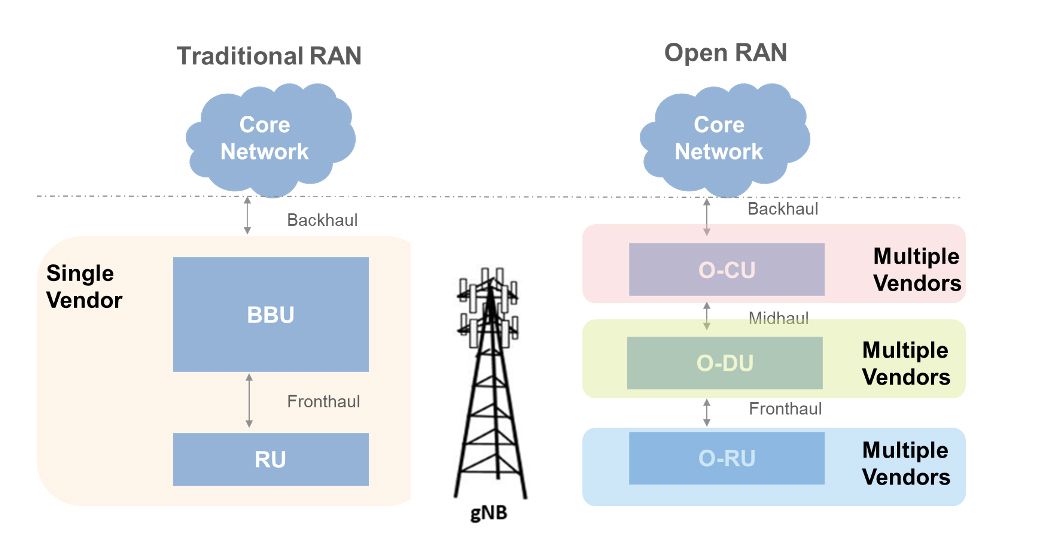
Open RAN telecom networks need testing for each disaggregated component, but that’s not enough. End-to-end testing is also necessary. In How do Open RAN interfaces work?, we covered how Open RAN redefines traditional RAN architecture by disaggregating it into three primary components: the radio unit (RU), distributed unit (DU), and centralized unit (CU). This paradigm…
What is a private 5G network? How does it work?
Private networks have the potential to change many industries and become the primary application for 5G. Processes and protocols make them work.
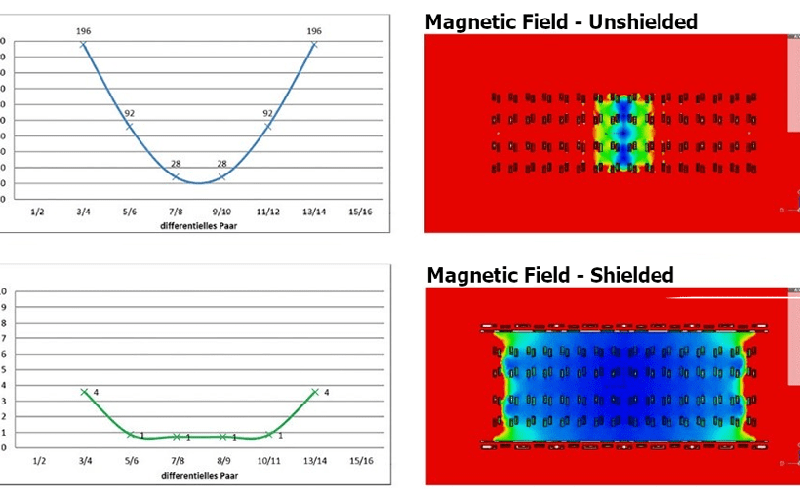
Why is signal integrity crucial for high-speed connector designs?
We discuss the importance of signal integrity, review high-speed deployment challenges, and highlight various connector design strategies to prevent distortion and degradation.
How do Open RAN interfaces work?
The O-RAN Alliance has developed specifications for communications interfaces between components of an Open RAN. This FAQ explains the functions of each.