The BGT60LTR11AIP from Infineon Technologies lets you add a 60-GHz motion sensor to embedded devices.
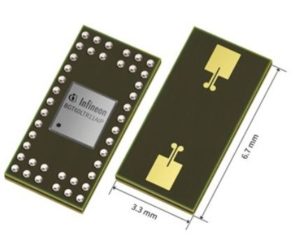 Engineers designing embedded devices often find themselves needing to add human presence and motion sensing capabilities even when RF isn’t their primary focus. Infineon’s BGT60LTR11AIP Radar sensor provides the transmitter, receiver, signal processing, and antennas into what the company claims is its smallest package for such a device.
Engineers designing embedded devices often find themselves needing to add human presence and motion sensing capabilities even when RF isn’t their primary focus. Infineon’s BGT60LTR11AIP Radar sensor provides the transmitter, receiver, signal processing, and antennas into what the company claims is its smallest package for such a device.
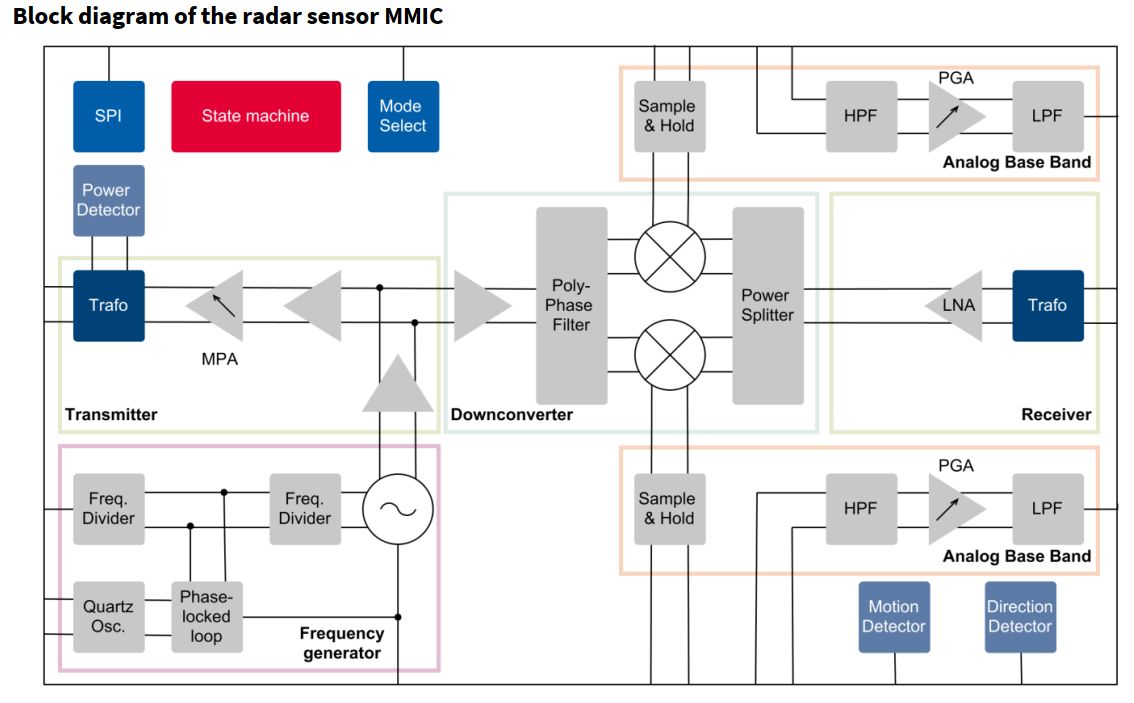
Measuring 3.3 mm × 6.7 mm @times; 0.56 mm, the BGT60LTR11AIP operates at 60 GHz (58 GHz to 62 GHz). The device provides two transmit channels and four receive channels through the package’s one transmit antenna and one receive antenna. The BGT60LTR11AIP can detect a person at a distance up to 7 m with resolution to 2.5 cm. The device also operates as a motion detector and direction sensor. Because the BGT60LTR11AIP includes a state machine (see block diagram, click to enlarge), it can operate in devices without an external microcontroller.
When operating in autonomous mode, the BGT60LTR11AIP needs just a few external components: a crystal, low-dropout (LDO) regulator, resistors, and capacitors. Infineon supplies the BGT60LTR11AIP shield board for evaluation purposes. The shield board can mount atop MCU7 Radar baseboard, which adds a USB post, demo software, and a GUI. If you need a separate microcontroller, the sensor can communicate over an SPI bus.
You can design the BGT60LTR11AIP into products for smart homes such as appliances, gesture detection, robotics, lighting, and door openers. It can function as a “wake-up” device when it detects motion.




Tell Us What You Think!