Extend the reach of Ethernet by converting the signals to different electrical or optical signals.
Ethernet extenders and media converters can both be used to expand network coverage. Extenders operate over unshielded twisted pair (UTP) or coaxial cabling, while media converters change the signals from electrical to optical and back. Extenders and media converters can also be used to add power over Ethernet (PoE) capability or to add redundancy to networks.
A typical Ethernet extender converts Ethernet to digital subscriber line (DSL) for long-distance transmission over various types of copper such as coax, twisted pairs such as Cat 5e/6/7, RS-232, RS-422, RS-485, closed circuit television (CCTV), and community access television (CATV) systems. Extenders can be used within facilities, within campuses with several buildings, and over longer distances (Figure 1).
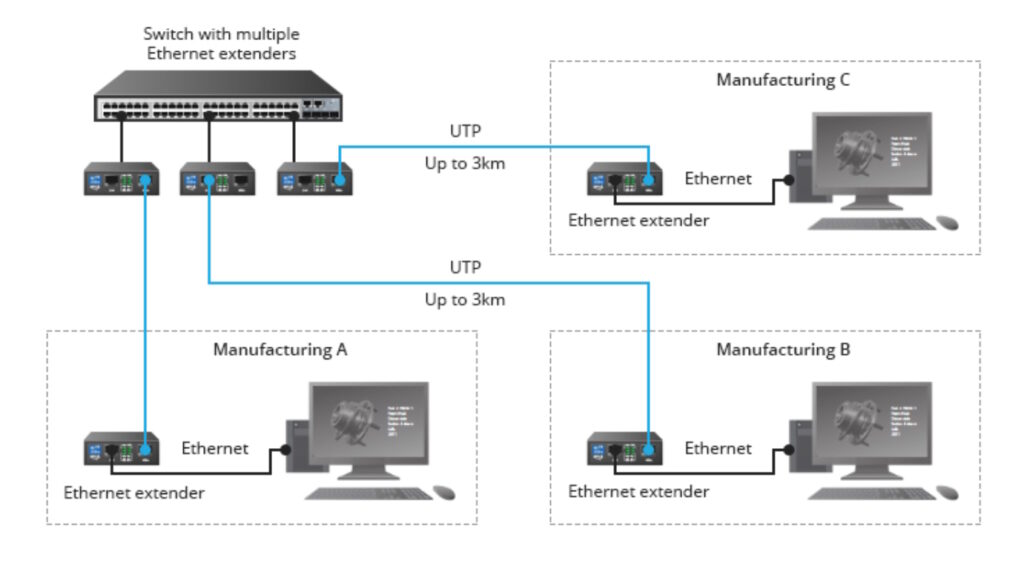
Figure 1. Ethernet extenders can be used to connect buildings on campus (Image: FS).
Faster speeds and longer distances
In addition to using DSL, extenders can use very high-speed digital subscriber line (VDSL) technology to extend 10/100/1000Base-T Ethernet up to 3 km or single-pair high-speed digital subscriber line (SHDSL), enabling 10/100Base-TX Ethernet to be transmitted up to 20 km. Media converters are available that can support 10/100/1000 Mb/sec or even 10 Gb/sec optical connectivity, with transmission distance up to 140 km. They are used in larger facilities, data centers, metro Ethernet networks, and similar applications that demand either very high transmission speeds, very long transmission distances, or a combination of both.
PoE converters and extenders
Media converters and extenders can expand the reach of PoE technology in addition to supporting longer data transmission distances. A basic PoE installation is limited to delivering power up to 100 m, which is sometimes insufficient.
For example, a media converter can be used to deliver data to a remote facility up to 140 km away. At the receiving end, a PoE media converter can convert the data back into Ethernet and inject PoE power into the UTP cabling (Figure 2). Because PoE can deliver power up to 100 m, powered devices can be up to 200 m apart, 100 m in opposite directions from the point of power injection.

Figure 2. Media converters are available with integrated PoE capabilities (Image: Omnitron Systems).
Dual fiber ports for daisy chaining and redundancy
Media converters, including PoE media converters, are available with dual fiber ports. Dual ports can be used for daisy chaining multiple powered devices (PDs) over a fiber route. Applications for daisy chaining include surveillance cameras and sensors around large campuses or along borders, pipelines, traffic monitoring systems, and railroad lines. Dual fiber ports are also used to provide redundant operation in high-availability systems. In redundant systems, the PoE switch senses when the primary fiber port becomes inactive and automatically switches to the backup fiber line in less than 50 ms (Figure 3).

Figure 3. Dual fiber ports on a media converter can be used to support daisy chaining (top) or redundancy (bottom) (Image: Omnitron Systems).
Summary
Ethernet extenders and media converters are useful devices for expanding the reach of networks. Extenders operate with electrical signals, while converters create fiber interconnects that can support higher data rates over longer distances. Media converters and extenders can integrate PoE functionality to deliver power as well as data. Media converters with dual fiber ports can be used to support redundant operation for high availability systems and daisy chaining to support networks spread over hundreds of kilometers.
References
Ethernet Media Converter vs Ethernet Extender, Versitron
How To Extend Distances to PoE Devices, Omnitron Systems
Media Converter vs Ethernet Extender, FS




Tell Us What You Think!